|
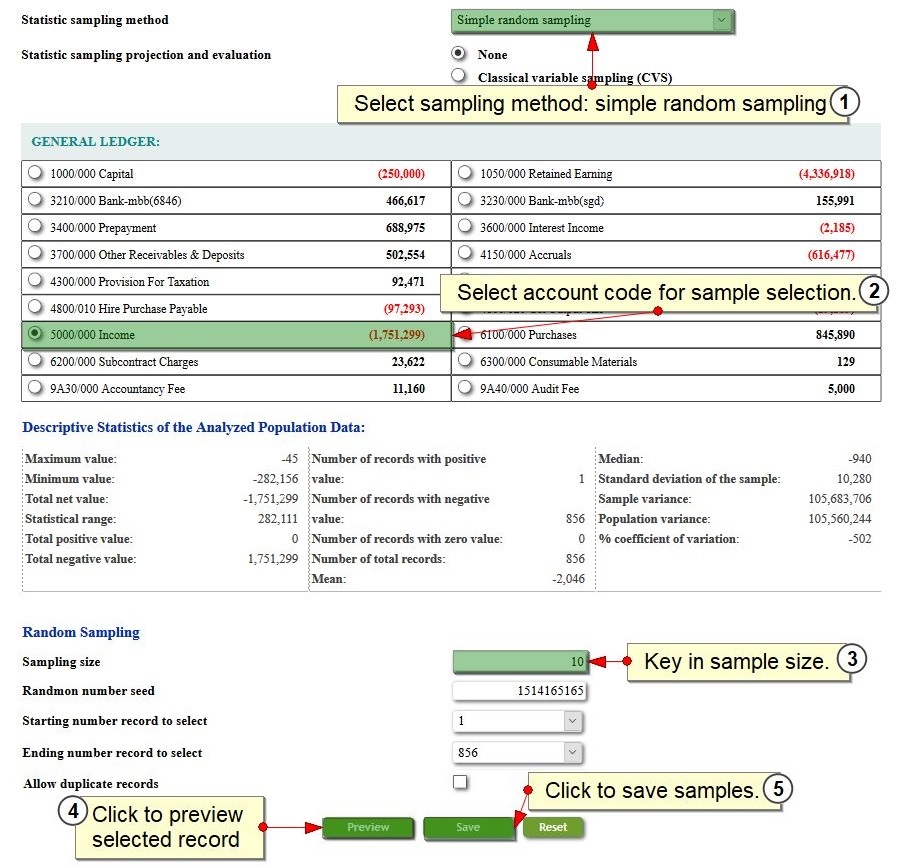
Simple Random Sampling
Every item in the population has equal chances of being selected as samples.
Random sample results in a statistically unbiased sample that may or may not be a representative sample.
Avoid using random sampling if audit objective is to detect over-statement of a class of transaction or balance, stratification or MUS is more appropriate.
Random sampling is usually to be used in conjunction with classical variable sampling (CVS) for projection and evaluation.
|